Long daytime naps might raise your odds for A-fib
القيلولة لأكثر من 30 دقيقة يوميا تزيد من عدم انتظام ضربات القلب
medicalxpress
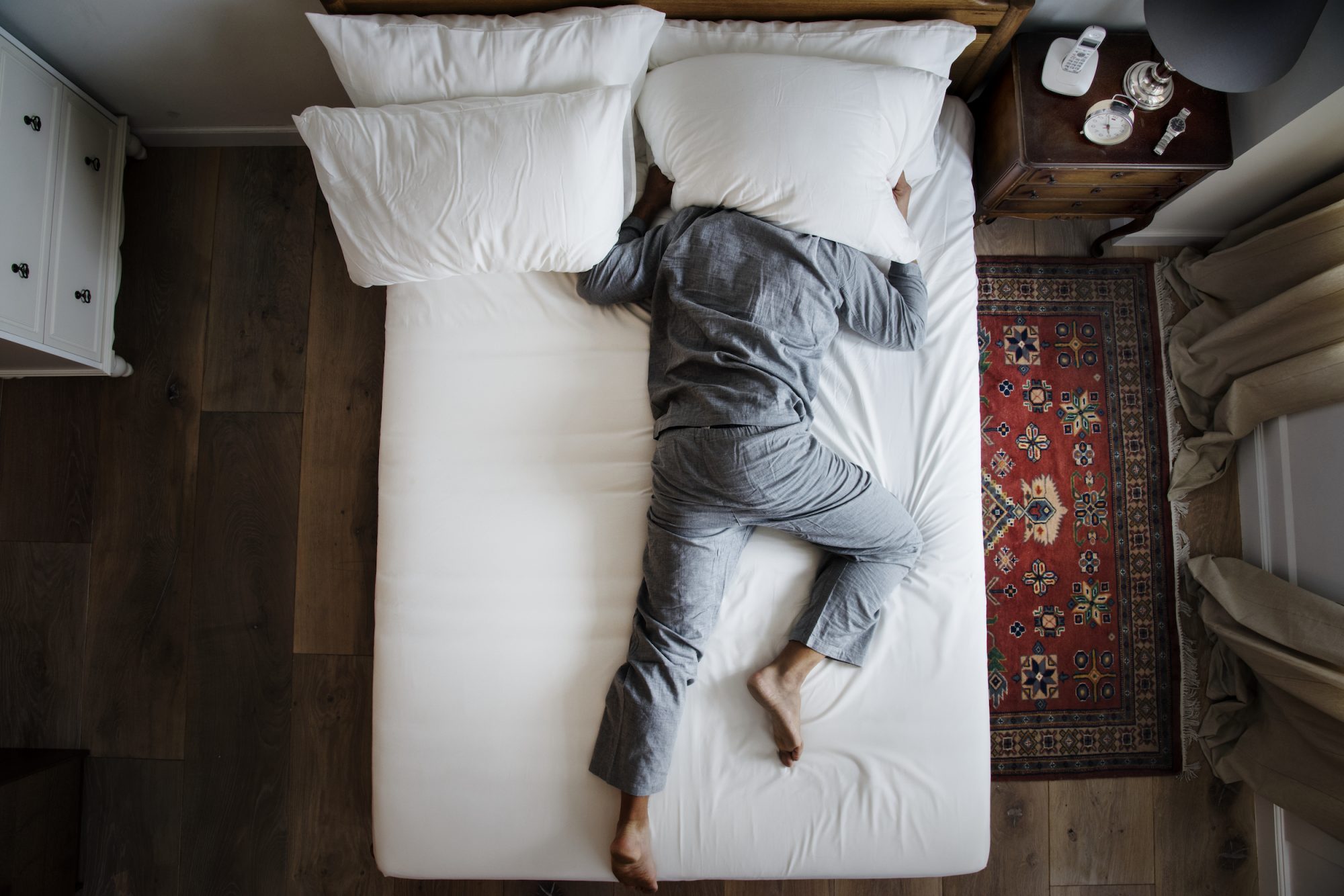
Madrid: Daytime naps longer than a half-hour appear to nearly double a person’s risk of developing an irregular heartbeat, a new study reports.
People who nap 30 minutes or more a day have a 90% higher risk of developing the heart rhythm disorder atrial fibrillation (a-fib) than those who take shorter naps, according to research presented Thursday at a meeting of the European Society of Cardiology, in Malaga, Spain.
“Our study indicates that snoozes during the day should be limited to less than 30 minutes,” study author Dr. Jesus Diaz-Gutierrez of Juan Ramon Jimenez University Hospital in Huelva, Spain, said in a society news release. “People with disturbed night-time sleep should avoid relying on napping to make up the shortfall.”
Research presented at meetings should be considered preliminary until published in a peer-reviewed journal.
A-fib causes the heart’s upper chambers to beat irregularly, increasing a person’s risk of stroke fivefold, the researchers said in background notes. It’s the world’s most common heart rhythm disorder.
For this study, the investigators tracked more than 20,000 Spanish university graduates. Participants were divided into three groups: those who don’t nap; those who nap less than 30 minutes; and those who nap 30 minutes or more each day.
During an average follow-up of nearly 14 years, 131 participants developed a-fib.
Those taking longer naps had nearly twice the risk of atrial fibrillation compared to those taking short naps, according to the first analysis. Meanwhile, folks who didn’t nap did not have any elevated a-fib risk compared to short-nappers.
Looking more closely at short-nappers, the researchers found that those who napped for fewer than 15 minutes had a 42% lower risk of developing a-fib, while those who napped 15 to 30 minutes had a 56% reduced risk compared with long nappers.
“The results suggest that the optimal napping duration is 15 to 30 minutes,” Diaz-Gutierrez said. “Larger studies are needed to determine whether a short nap is preferable to not napping at all.”
He said there are many potential explanations for the link between napping and health.
“For example, long daytime naps may disrupt the body’s internal clock (circadian rhythm), leading to shorter night-time sleep, more nocturnal awakening and reduced physical activity,” he said. “In contrast, short daytime napping may improve circadian rhythm, lower blood pressure levels and reduce stress.”
While the study found an association between naps and a-fib risk, it could not prove cause and effect.
قنا
مدريد: كشفت دراسة جديدة أن قيلولة لمدة 30 دقيقة كل يوم قد تزيد من خطر عدم انتظام ضربات القلب والرجفان الأذيني، وهي حالة قلبية تؤدي إلى عدم انتظام ضربات القلب وغالبا ما تكون سريعة بشكل غير طبيعي.
وتشير نتائج الدراسة إلى أن مدة القيلولة المثلى هي من 15 إلى 30 دقيقة.
وقال الدكتور دياز جوتيريز من مستشفى /خوان رامون خيمينيز/ الجامعي في إسبانيا: “أشارت الدراسات السابقة إلى أن أنماط النوم قد تلعب دورا في تطوير الرجفان الأذيني، بينما تشير الدراسة الحالية إلى أن فترات الغفوة أثناء النهار يجب أن تقتصر على أقل من 30 دقيقة”.
وأضاف أن هناك العديد من التفسيرات المحتملة للعلاقة بين القيلولة وصحة القلب، حيث قد تؤدي قيلولة النهار الطويلة إلى تعطيل الساعة الداخلية للجسم مما يؤدي إلى نوم أقصر ليلا، والاستيقاظ أكثر أثناء الليل وتقليل النشاط البدني.
ولمعرفة ما إذا كان من الممكن ربط القيلولة بالحالة، حلل الباحثون بيانات أكثر من 20000 شخص لم تكن لديهم ضربات قلب غير منتظمة.
وقام المشاركون بملء استبيان كل عامين وتم تصنيفهم إلى ثلاث مجموعات وفقا لمتوسط مدة القيلولة اليومية – لا شيء، أقل من 30 دقيقة أو 30 دقيقة وأكثر. ومقارنة بمن ينامون لفترة قصيرة خلال النهار، فإن أولئك الذين يغفون لمدة 30 دقيقة أو أكثر يوميا لديهم خطر مضاعف تقريبا للإصابة بالرجفان الأذيني.
وكشف التحليل الإضافي أن وقت القيلولة المثالي يبدو ما بين 15 و30 دقيقة، حيث كان لدى هؤلاء الأشخاص مخاطر أقل بنسبة 56% لتطوير ضربات قلب غير منتظمة مقارنة بأولئك الذين غفوا لمدة نصف ساعة أو أكثر.
يشار إلى أن أكثر من 40 مليون شخص في جميع أنحاء العالم يصابون بالرجفان الأذيني، ويتعرض المصابون به إلى خمسة أضعاف خطر الإصابة بالسكتة الدماغية مقارنة بأقرانهم.