Federal Reserve stops normalization of monetary policy
الاحتياطي الفيدرالي يوقف تطبيع السياسة النقدية
The US Federal Reserve, widely known as simply ‘the Fed,’ has struck again, with the 19-20 March meeting of its Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC) providing yet another dovish surprise to markets. After nine rate hikes since December 2015, the latest two FOMC meetings have produced one of the most notable sudden monetary policy changes in recent years.
In a few months, the Fed has gone from steady interest rate hikes with continuous runoff of assets from its balance sheet to a patient wait-and-see approach. As per the new guidance, rate movements are data dependent and the asset runoff, otherwise known as quantitative tightening (QT), is set to quickly taper before a full stop.
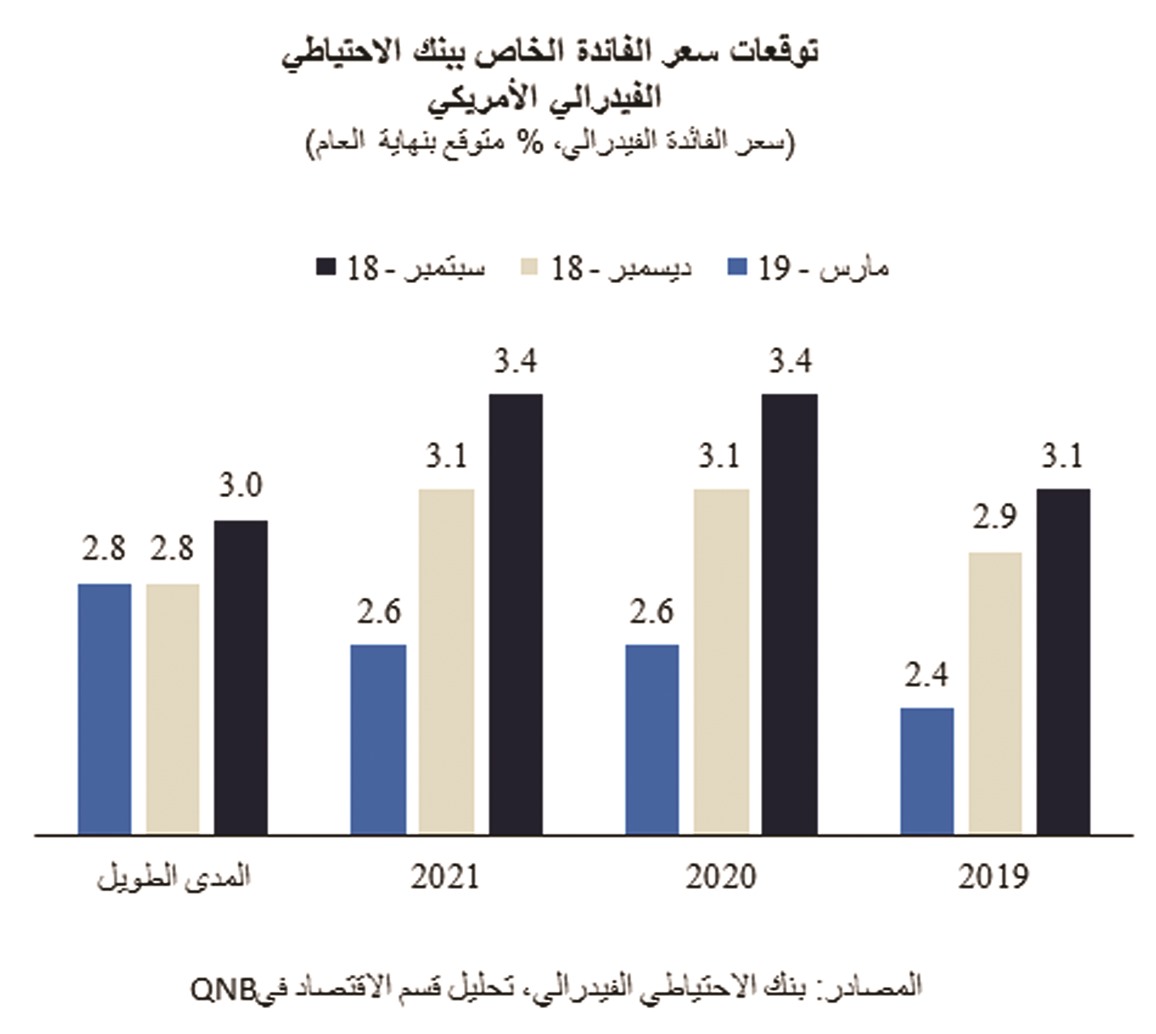
The interest rate projection of Fed officials moved to suggest that the FOMC will not increase interest rates in 2019 and only enact one more modest hike over the next two years. Importantly, the ‘no hike’ expectation for this year was set by a 11-6 majority, suggesting a strong support for the dovish position within the FOMC.
Moreover, the Fed has decided to stop QT by September 2019, effectively supporting an ample supply of reserves and therefore limiting future drags on liquidity. The decision has come amidst rising downside risks for global growth, muted inflation pressures and inflation expectations, and concerns over financial stability.
Markets have reacted strongly to the Fed’s dovish pivot. The implied probability of rate hikes in any of the remaining 2019 FOMC meetings has plummeted from more than 90.0% in October 2018 to around 6.0 percent after the January 2019 meeting and 0.0% at the time of writing. Perhaps even more telling is that bond markets have started to price in potential rate cuts. The implied probability of rate cuts in Q4 2019 surged from zero late last year to over 50% after the March 2019 FOMC meeting.
In fact, as of now, the Fed, expert consensus and bond markets diverge considerably about the future path of fed funds rate. While both the Fed and leading experts point to moderate hikes either late this year or at some point next year, future markets are implying rate cuts as soon as this year.
As fed funds rate nears estimates of the neutral rate or the rate that separates accommodative from restrictive policy, uncertainty grows about both the timing and the direction of monetary policy.
In our view, the fed funds rate is going to remain flat in 2019 or at any time in the foreseeable future. There are two main reasons why we do not see a compelling reason for rate cuts, bond markets notwithstanding.
First, the overall US growth story is currently being clouded by rather temporary Q1 2019-related idiosyncratic factors, including residual seasonality, an inventory overhang, a corporate earning recession and an unusually long government shutdown.
US GDP growth is expected to rebound in Q2 to 2.6 percent q/q annualized growth from 1.5 percent in Q1. Despite a fading fiscal stimulus and mounting concerns of slowing growth in Europe and China, the US economic performance is still robust. Growth is expected to gradually stabilize slightly above potential or trend (around 1.9 percent) after Q2. The unemployment rate is around multi-decade lows and average hourly earnings growth continues to pick up to near pre-great financial crisis rates.
Second, broader financial conditions have eased significantly in recent months, which are expected to produce positive lagged effects on GDP over the coming quarters. According to the Bloomberg US Financial Condition Index, which tracks the overall level of stress in money, bond, and equity markets to help assess the availability and cost of credit, financial conditions have reversed from deep into restrictive territory in Q4 2018 back to accommodative territory this quarter. In other words, financial markets continue to do part of the job for the Fed, which lessens the pressure for future rate cuts.
All in all, the Fed is now quickly moving towards a full pause in monetary policy normalization. No more policy rate hikes are expected for this year and the QT process is set to end soon. From September 2018 to March 2019, the Fed has changed its projections for rate increases over 2019-2021 from four hikes or 100 basis points (bps) to one hike or 25 bps. Despite domestic and external headwinds, bond market expectations about rate cuts already in 2019 are rather premature.
قالت مجموعة «QNB» في تقريرها الاقتصادي الأسبوعي أن بنك الاحتياطي الفيدرالي الأميركي قد أكد مجدداً موقفه المتساهل، حيث قدم مفاجأة أخرى للأسواق في اجتماع اللجنة الفيدرالية للسوق المفتوح، الذي عقد في 19 و20 مارس. فبعد تسع جولات من رفع أسعار الفائدة منذ ديسمبر 2015، انتقل بنك الاحتياطي الفيدرالي إلى نهج متأني يعتمد على الانتظار والترقب. ووفقًا للتوجه الجديد، سيعتمد تغيير أسعار الفائدة على البيانات، ويُنتظر أن يتم إكمال برنامج التخفيض التدريجي للأصول، الذي يشار إليه أيضاً بالتشديد الكمي، بسرعة قبل إنهائه بالكامل.
تفاعل
وتفاعلت الأسواق بقوة مع الموقف المتساهل لبنك الاحتياطي الفيدرالي. فقد تراجع احتمال رفع أسعار الفائدة في الاجتماعات المتبقية للجنة الفيدرالية للسوق المفتوح في عام 2019 من أكثر من 90% في أكتوبر 2018 إلى 0% حالياً. ولعل المؤشر الأكثر دلالة في هذا الخصوص هو أن أسواق السندات بدأت تتوقع تخفيض أسعار الفائدة، حيث ارتفع احتمال خفض أسعار الفائدة خلال الربع الأخير من 2019 من صفر في أواخر العام الماضي إلى أكثر من 50% بعد اجتماع اللجنة الفيدرالية للسوق المفتوح.
استقرار
وقال تقرير «QNB»: في نظرنا، فإن سعر الفائدة الرئيسي لبنك الاحتياطي الفيدرالي الأميركي سيظل دون تغيير في 2019 وفي المستقبل القريب. وهناك سببان رئيسيان يجعلان تخفيض أسعار الفائدة أقل إلحاحاً، بصرف النظر عن توقعات أسواق السندات.
أولاً، يتأثر حاليًا مشهد النمو الكلي في الولايات المتحدة ببعض العوامل الخاصة والمؤقتة، وهي مرتبطة بالربع الأول من 2019، ومن بينها التأثيرات الموسمية المتبقية، وتكدس المخزون، وتراجع عائدات الشركات، والإغلاق الحكومي الطويل بشكل غير معتاد. ومن المتوقع أن ينمو الاقتصاد الأميركي في الربع الثاني إلى 2.6% على أساس ربع سنوي. وعلى الرغم من تلاشي تأثير التحفيزات المالية وتزايد القلق بشأن تباطؤ النمو في أوروبا والصين، فإن الأداء الاقتصادي في الولايات المتحدة لا يزال قوياً. ومن المتوقع أن يستقر النمو تدريجياً بعد الربع الثاني عند 1.9%.
الأوضاع المالية
ثانياً، أصبحت الأوضاع المالية العامة ميسرة بشكل كبير في الأشهر الأخيرة، ويُتوقع أن يكون لذلك تأثيرات إيجابية متأخرة على الناتج المحلي الإجمالي خلال الفترة القادمة. ووفقاً لمؤشر «بلومبيرج» للوضع المالي في الولايات المتحدة، والذي يتتبع مستوى الضغط الكلي في أسواق المال والسندات والأسهم للمساعدة في تقييم مدى توافر وتكلفة الائتمان، فإن الأوضاع المالية قد انتقلت من المنطقة المشددة للغاية إلى المنطقة المشددة في الربع الأخير من عام 2018، ثم إلى المنطقة الميسرة في الربع الحالي.